Regenerative therapies revolutionize healthcare by activating cells to repair tissues and organs, with non-invasive diagnostics playing a crucial role in patient assessment and treatment monitoring. Advanced imaging techniques (like MRI and ultrasound) and biomarker analysis enable early detection of tissue damage, personalized interventions, and continuous tracking of therapeutic progress without causing harm. Molecular markers detected through these non-invasive methods provide insights into treatment effectiveness, facilitating precise, ethical, and responsible regenerative therapy practices.
Regenerative therapies offer a promising frontier in medicine, harnessing the body’s inherent ability to heal. This article delves into the crucial aspect of accurate assessment for these innovative treatments. From understanding their potential to exploring advanced imaging and molecular markers, we scrutinize every angle. We emphasize the pivotal role of non-invasive diagnostics, enabling safe, effective evaluation without patient risk. Moreover, ethical considerations and future directions are discussed, painting a comprehensive picture for healthcare professionals navigating this game-changing field.
- Understanding Regenerative Therapies and Their Potential
- The Role of Non-Invasive Diagnostics in Assessment
- Advanced Imaging Techniques for Regenerative Medicine
- Molecular Markers and Their Significance in Evaluation
- Ethical Considerations and Future Directions for Accurate Assessment
Understanding Regenerative Therapies and Their Potential

Regenerative therapies represent a groundbreaking approach in medicine, harnessing the body’s inherent ability to heal and regenerate itself. These innovative treatments go beyond traditional methods by stimulating and activating the patient’s own cells to repair damaged tissues and organs. The potential of regenerative therapies is vast, offering promising solutions for various conditions previously considered incurable or requiring invasive procedures.
By integrating non-invasive diagnostics, healthcare professionals can accurately assess a patient’s eligibility and response to these therapies. Advanced imaging techniques and biomarker analysis enable the early detection of tissue damage and the monitoring of cellular responses during treatment. This precision approach ensures that regenerative interventions are tailored to individual needs, maximizing their therapeutic potential while minimizing risks associated with unnecessary procedures.
The Role of Non-Invasive Diagnostics in Assessment
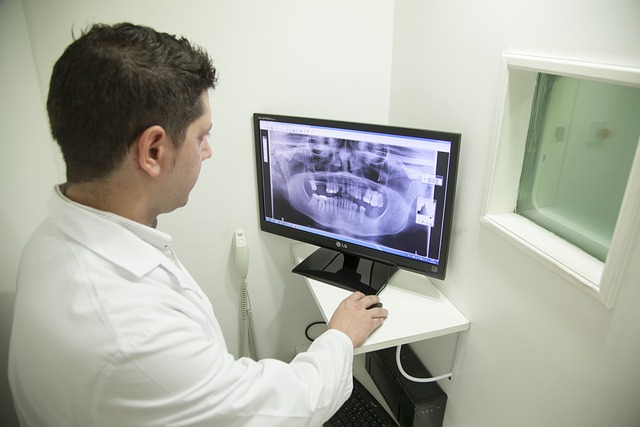
The advancement of regenerative therapies requires precise and effective assessment tools, which is where non-invasive diagnostics play a pivotal role. These cutting-edge technologies offer a less intrusive approach to evaluating patient conditions while providing valuable insights into the success and progress of therapeutic interventions. By employing non-invasive methods, healthcare professionals can assess tissue regeneration, monitor cell growth, and detect early signs of improvements or potential complications without causing additional harm.
Non-invasive diagnostics encompass a range of techniques such as advanced imaging, biomarker analysis, and molecular diagnostics. For instance, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound provide detailed images of internal structures, enabling doctors to track changes in tissue architecture over time. Biomarkers, on the other hand, offer quantitative measures of specific biological processes or substances related to regeneration. These tools collectively contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s response to regenerative therapies, ultimately guiding personalized treatment plans.
Advanced Imaging Techniques for Regenerative Medicine
The field of regenerative medicine is revolutionizing healthcare with its potential to repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs. Advanced imaging techniques play a pivotal role in this process, offering non-invasive diagnostics that enable precise assessment of regenerative therapies. Technologies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasonography provide detailed visualizations of the body’s internal structures, allowing doctors to monitor the progress of tissue regeneration and identify any potential complications early on.
For instance, MRI can offer high-resolution images of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments, which are often targets for regenerative interventions. This non-invasive approach helps in tracking the formation of new blood vessels, collagen production, and overall tissue remodeling without the need for invasive biopsies. Similarly, ultrasonography is valuable for real-time assessment of cell transplantation and the development of new functional tissues, ensuring that regenerative therapies align with desired outcomes.
Molecular Markers and Their Significance in Evaluation

Molecular markers play a pivotal role in the accurate assessment and evaluation of regenerative therapies. These tiny biological signatures, detected through advanced non-invasive diagnostics techniques, offer profound insights into the body’s response to treatments designed to regenerate tissues and organs. By analyzing specific molecules present or produced during therapy, healthcare professionals can gauge the effectiveness of interventions, track progress, and even predict potential outcomes.
The significance lies in their ability to provide objective, measurable data without causing discomfort or requiring invasive procedures. This non-invasive approach allows for repeated monitoring throughout the therapeutic process, enabling timely adjustments to treatment plans based on real-time biological feedback. As such, molecular markers serve as a powerful tool for advancing regenerative medicine by ensuring treatments are tailored to individual patient needs and optimized for maximum efficacy.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions for Accurate Assessment

The pursuit of accurate assessment in regenerative therapies necessitates a careful balance between scientific rigor and ethical considerations. As non-invasive diagnostics gain traction, researchers must ensure these methods are not only effective but also respect patient autonomy and privacy. The implementation of cutting-edge technologies, such as advanced imaging techniques and biomarkers, presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, these tools offer enhanced precision in monitoring therapeutic responses; on the other, they raise questions about data security and informed consent. Striking a chord between innovation and ethical boundaries is crucial to foster public trust and ensure the responsible advancement of regenerative medicine.
Looking ahead, future directions for accurate assessment should focus on integrating diverse non-invasive diagnostics to create comprehensive evaluation frameworks. Collaborative efforts between multidisciplinary teams, including medical professionals, bioethicists, and technology developers, will be pivotal in addressing these complex ethical issues. By fostering a culture of transparency and rigorous standards, the field can harness the potential of innovative assessments while upholding the highest ethical standards, ultimately shaping the future of regenerative therapies for the better.
Regenerative therapies hold immense potential to revolutionize medical treatments, but accurate assessment is key. Integrating non-invasive diagnostics, advanced imaging techniques, and molecular markers allows for comprehensive evaluation, enhancing patient outcomes and ensuring ethical practices. As research progresses, these tools will continue to play a vital role in navigating the complex landscape of regenerative medicine, fostering advancements that promise a brighter future for many.
